Real-Time LoRaWAN Traffic Analyzer for ChirpStack
Why Monitor LoRaWAN Traffic
Running a few gateways gives you a window into everything happening on the LoRaWAN spectrum in your area -- not just your own devices, but every transmission your gateways pick up. Most people never look at this data. They configure their devices, check that uplinks arrive, and move on.
That's a missed opportunity. Your gateways hear traffic from dozens of operators and hundreds of devices. Understanding who's transmitting, how often, on which channels, and at what spreading factors reveals how congested the spectrum actually is in your area. It also catches problems with your own devices -- packet loss, drifting frame counters, unexpected spreading factor changes -- before they become outages.
The problem: ChirpStack shows you your own devices well, but doesn't give you the full picture of everything your gateways receive. I built an open-source traffic analyzer that does.
The analyzer is open source and available on GitHub: https://github.com/1rabbit/lorawan-analyzer
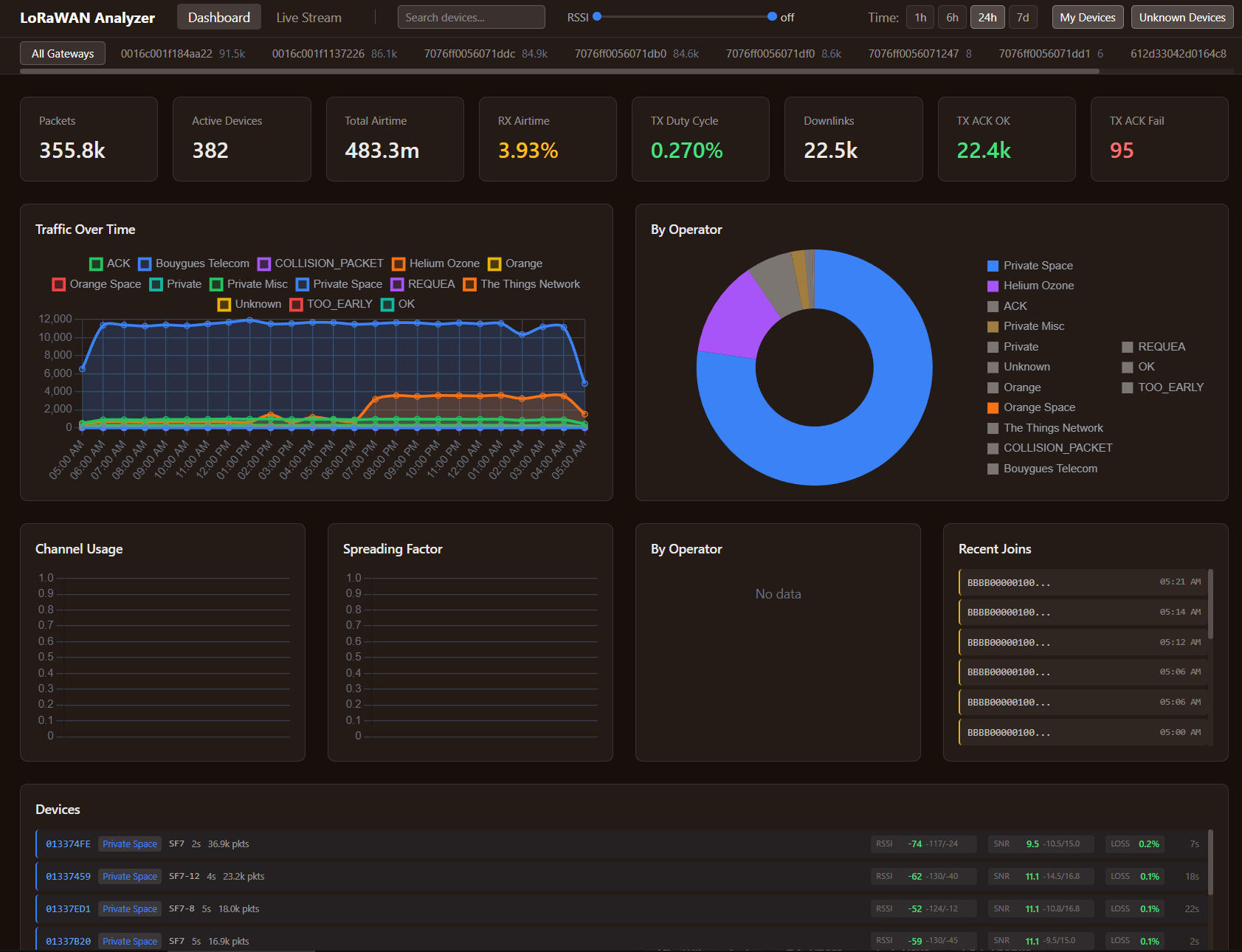
What It Does
The analyzer connects directly to your ChirpStack MQTT broker, captures all gateway events -- uplinks, downlinks, join requests, TX acknowledgements -- stores them in ClickHouse, and serves a web dashboard.
Gateway and device navigation:
A tree view organizes traffic by gateway, then by operator, then by individual device. Every device address gets automatically mapped to its operator using the built-in LoRa Alliance NetID database covering 175+ operators. You see at a glance which operators have devices in range of your gateways and how much traffic each generates.
Per-device analytics:
Drill into any device -- yours or foreign -- and see frame counter timelines with gap detection (revealing packet loss), RSSI and SNR trends over time, transmission interval histograms, and distributions across spreading factors, frequencies, and gateways. For your own devices, this is detailed diagnostic data. For foreign devices, it reveals how other operators' deployments behave in your area.
Spectrum view:
Channel usage distribution, spreading factor breakdown, and duty cycle tracking across your gateways. This answers the question every LoRaWAN operator should ask: how busy is the spectrum in my area, and which channels are most congested?
Operator identification:
The built-in NetID database automatically identifies which operator owns each device based on its DevAddr. Custom prefix rules let you label your own networks and separate "my devices" from foreign traffic in every view.
Join request tracking:
Join requests grouped by JoinEUI with manufacturer lookup and timeline visualization. Useful for spotting devices that keep re-joining (indicating connectivity problems) or identifying new devices appearing in your area.
Live packet feed:
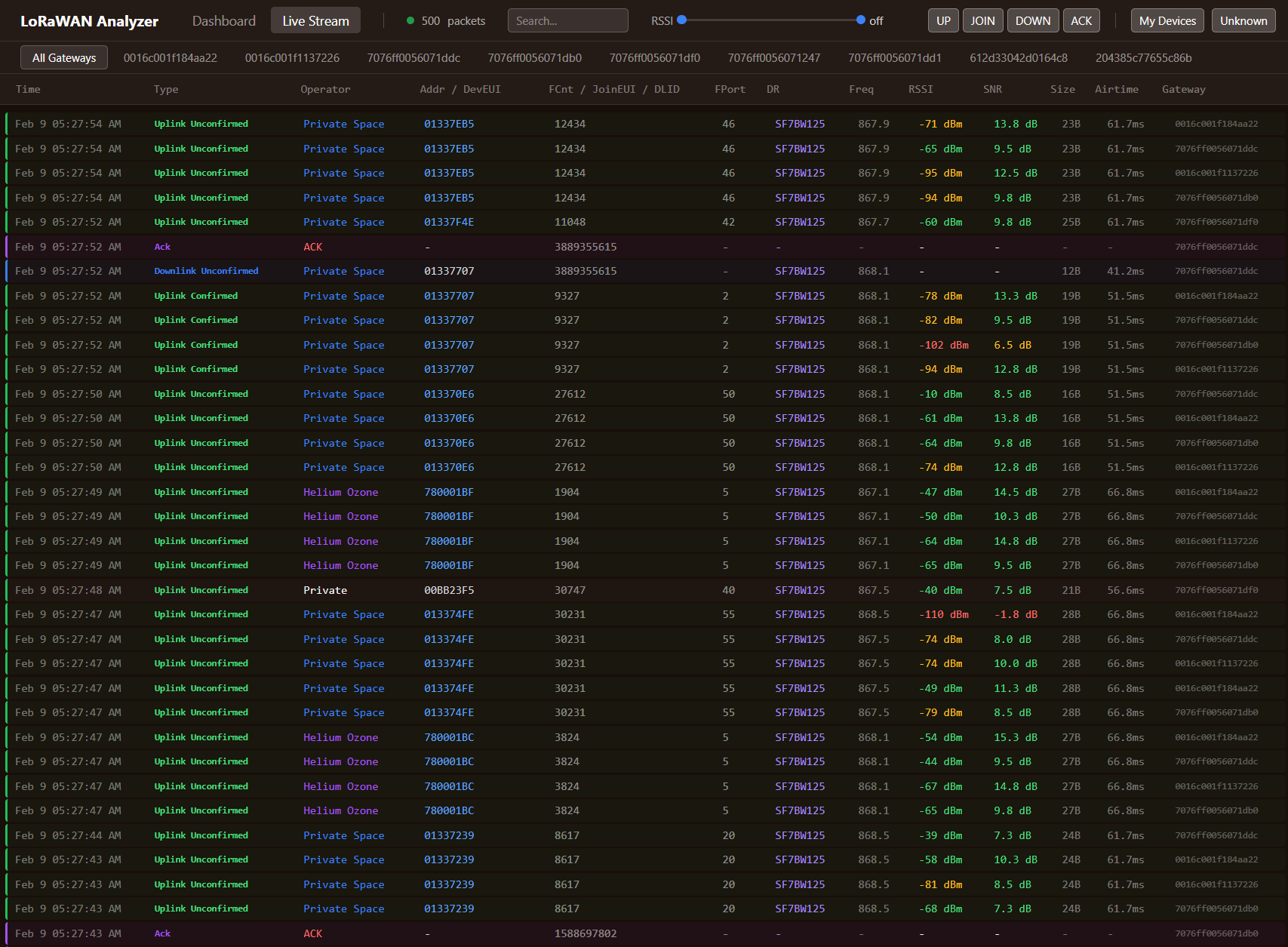
Real-time WebSocket stream showing every packet as it arrives. Filter by packet type, RSSI range, or ownership. Useful for watching device behavior during commissioning or troubleshooting.
Session tracking and airtime:
The analyzer correlates join requests with subsequent data uplinks, tracking device sessions. Per-packet airtime calculation based on Semtech SX1302 datasheet formulas gives accurate duty cycle accounting.
Setup
Three commands. The analyzer runs as Docker containers alongside your existing ChirpStack installation.
cp config.toml.example config.toml
# edit mqtt.server to point at your ChirpStack MQTT broker
docker compose up -d
This starts two containers: the analyzer (web dashboard + API on port 15337) and ClickHouse (time-series storage, internal only). Dashboard is at localhost:15337. Packets appear as soon as gateways publish to the broker.
MQTT configuration:
The analyzer connects to the same MQTT broker that ChirpStack Gateway Bridge publishes to. No extra MQTT server needed. Point it at your existing broker:
[mqtt]
server = "tcp://your-chirpstack-mqtt:1883"
topic = "eu868/gateway/+/event/up"
format = "protobuf"
Supports both protobuf (ChirpStack v4) and JSON (v3) message formats. The region prefix in the topic must match your Gateway Bridge configuration.
Custom operator labels:
Define your own networks to separate your traffic from everyone else's:
[[operators]]
prefix = "26000000/20"
name = "My Network"
known_devices = true
color = "#3b82f6"
Multi-Instance Aggregation
Running multiple ChirpStack instances across different sites? Enable the bundled Mosquitto broker to aggregate traffic from all of them into a single dashboard:
docker compose --profile multiplex up -d
This adds a Mosquitto container on port 15338. Configure MQTT bridges on each ChirpStack instance to forward gateway events to this central broker. One dashboard, all your gateways, all your sites.
Technical Stack
- Backend: Node.js / TypeScript / Fastify
- Database: ClickHouse for time-series storage -- handles millions of packets efficiently
- Frontend: Vanilla JS + Chart.js -- fast, no framework overhead
- Deployment: Docker Compose -- self-contained, no external dependencies
ClickHouse was chosen over InfluxDB or PostgreSQL for this use case because LoRaWAN traffic analysis involves heavy aggregation queries across large datasets -- counting packets by operator, computing distributions across spreading factors and channels, detecting frame counter gaps. ClickHouse handles these analytical queries significantly faster than alternatives at the data volumes a busy gateway generates.
Use Cases
Spectrum congestion assessment:
Before deploying new devices, understand how busy the spectrum is in your area. The analyzer shows channel usage, spreading factor distribution, and duty cycle across all traffic your gateways see -- not just your own. This data drives decisions about device transmission intervals, spreading factor selection, and whether additional gateways are needed to handle the load.
Network troubleshooting:
Frame counter gaps reveal packet loss. RSSI/SNR trends over time expose environmental changes affecting coverage -- new buildings, vegetation growth, antenna degradation. Interval histograms show whether devices transmit on schedule or drift. Spreading factor distributions flag devices falling back to SF12 when they should be on SF7.
Foreign traffic monitoring:
Know who else is using the spectrum in your area. The operator identification database maps every device to its network. Track how many devices each operator runs, their traffic patterns, and their impact on shared channel capacity. This information matters for capacity planning in dense deployments.
Device commissioning:
The live feed lets you watch packets arrive in real time during device installation. Verify the device joins successfully, transmits at the expected interval, and achieves reasonable signal quality -- all without switching between ChirpStack tabs.
What I Provide
Services:
- Traffic analyzer deployment and configuration for your ChirpStack infrastructure
- Custom operator mapping and network labeling
- Multi-site aggregation setup with MQTT bridging
- Spectrum analysis and congestion assessment based on collected data
- Network optimization recommendations derived from traffic patterns
- Integration with existing monitoring infrastructure (Grafana, alerting)
You own everything:
- Self-hosted open-source software (MIT licensed)
- Complete configuration and deployment documentation
- All collected traffic data in your own ClickHouse database
- No vendor lock-in, recurring fees, or external dependencies
The analyzer is open source and available on GitHub. I help with deployment, configuration for your specific infrastructure, and interpreting the data it collects to make informed decisions about your LoRaWAN network.
Ready to Get Started?
Get expert guidance on implementing LoRaWAN solutions for your organization.
Let's Talk